Diagnosis
At the first onset of symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention in order to initiate treatment immediately and avoid more serious complications.
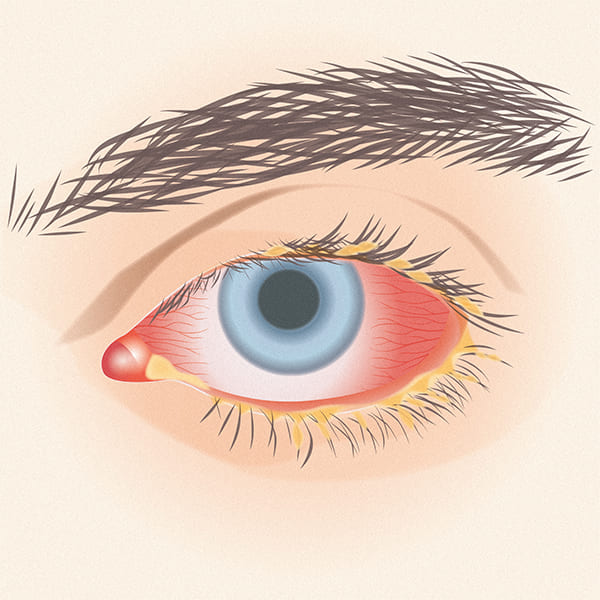
The diagnosis of bacterial conjunctivitis is made by the doctor or ophthalmologist, following an assessment of the symptoms and the appearance of the eye.
In the case of resistant or relapsing conjunctivitis, the specialist may suggest a conjunctival swab to search for the specific agent responsible for the infection and establish a targeted therapy.
Treatment
Treatment for bacterial conjunctivitis usually involves the prescription of antibiotic eye drops or ointments, which may or may not be combined with anti-inflammatory drugs.
Bacterial conjunctivitis has usually a short duration (it tends to resolve within 7-10 days), but symptoms may persist for a longer or shorter time, depending on the infectious agent that caused it, the timing of diagnosis and the effectiveness of treatment.
In addition, until the disease has resolved completely, it is important to prevent cohabitants and all those with whom one comes into contact from becoming infected by washing hands often and avoiding close contact or exchanging personal items.