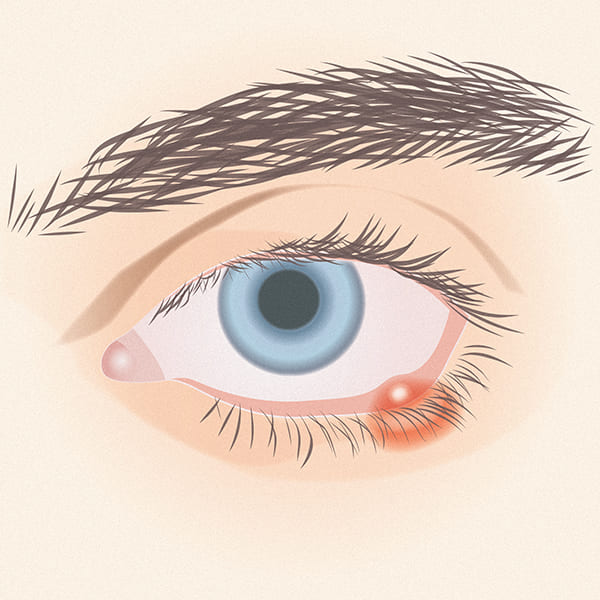
Diagnosis
If you suspect the presence of a stye, it is advisable to seek a diagnosis from your general practitioner or a specialist, an ophthalmologist, who will be able to indicate the best solution for your specific situation.
Treatment
Styes usually resolve spontaneously within a few days, without causing any vision damage. Generally, spontaneous rupture of the stye, with subsequent discharge of the pus, alleviates the symptoms and stimulates reabsorption.
In any case, it is important never to “squeeze” the stye as if it were a pimple, as this risks extending the infection and further irritating the eyelids.
To encourage spontaneous rupture of the stye, warm, wet compresses can be applied a couple of times a day with a cotton wool pad soaked in warm water or chamomile tea (which has a soothing effect) or with commercially available warming wipes. The compresses should not be excessively hot, otherwise there is a risk of further irritation of the eyelids.
In some cases the ophthalmologist may also prescribe an antibiotic ointment.