Diagnosis
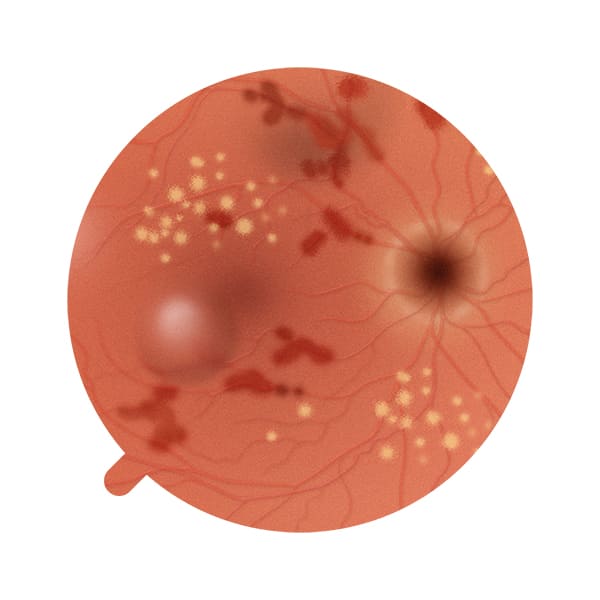
The diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy is made by a medical specialist, the ophthalmologist, following a check-up and after a careful analysis of the ocular fundus by means of specific examinations, such as fluorangiography, optical coherence tomography (OCT) and retinography.
It is important to bear in mind that, since it is a progressive disease, it is essential to diagnose diabetic retinopathy as early as possible to allow better management of the condition and prevent associated complications.
Treatment
The treatment of diabetic retinopathy varies depending on the stage of the disease and the individual’s general health.
The first essential treatment is careful blood glucose control, without which any treatment is only temporary. The ophthalmologist may also prescribe supplements whose ingredients have properties known to slow the progression or accelerate the repair of some of the changes induced in the retina by diabetes.
Should these occur, the specialist may prescribe one or more sessions of photocoagulation retinal laser therapy or intravitreal injections of specific drugs. In the case of retinal detachment, however, the treatment is usually a vitrectomy.