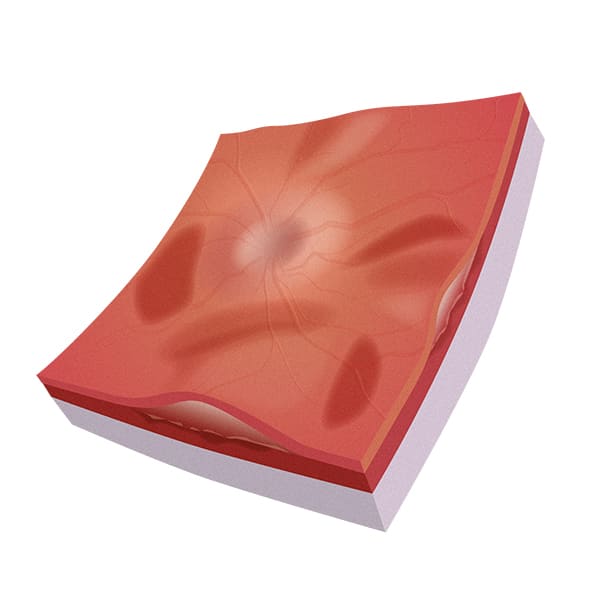
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of retinal oedema, in its two forms, macular or peripheral, is made by a medical specialist, the ophthalmologist, following a check-up and after a careful analysis of the ocular fundus, which can be further analysed through some specific examinations such as fluorangiography and optical coherence tomography (OCT).
Treatment
Treatment of retinal oedema varies depending on the cause, location and extent of the situation.
Systemic drugs (cortisone, antibiotics, immunosuppressants, etc.) may be prescribed to treat the underlying pathology causing the oedema.
In the case of macular oedema, the specialist may prescribe pharmacological treatment based on intravitreal injections of drugs aimed at limiting the alterations in the blood vessels that release fluid in the retina.
Peripheral oedema can instead be treated with laser photocoagulation. Support with retinotrophic or anti-inflammatory supplements may also be useful.