Diagnosis
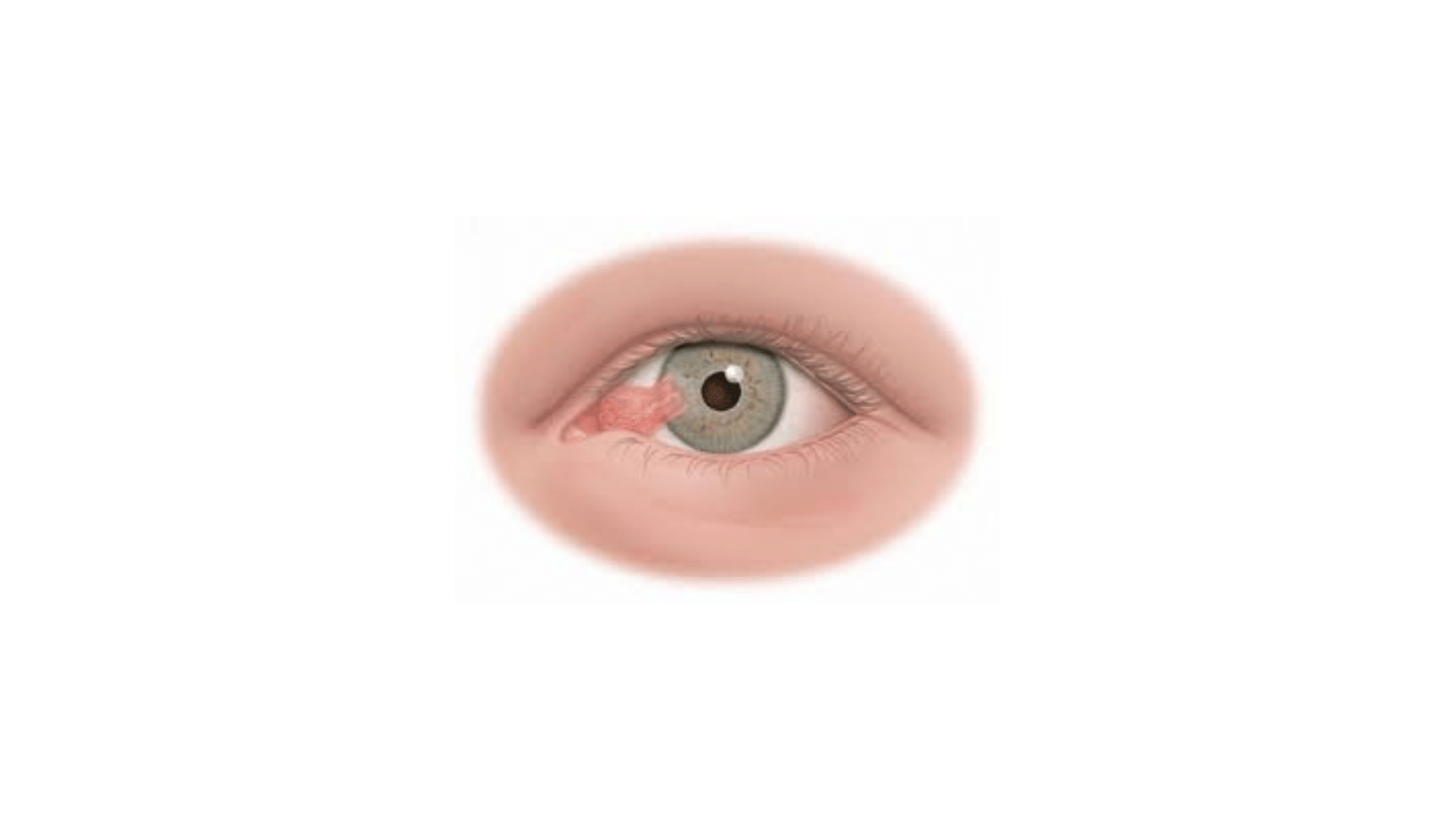
If you suspect the presence of a pterygium, you should seek a diagnosis from your primary care physician or a medical specialist, the ophthalmologist, who will be able to indicate the best course of action for each specific situation.
Treatment
The treatment of pterygium depends on the severity of the symptoms and the progression of the condition. In mild cases, where pterygium does not cause significant symptoms or visual disturbances, it may be sufficient to take some self-protective measures and monitor the situation closely. Here are some treatment options for pterygium:
1. Lubricating eye drops: Regular use of lubricating eye drops can help relieve symptoms of dryness or irritation caused by pterygium.
2. Sun protection: It is important to protect the eyes from intense sunlight and irritants. Wearing sunglasses that block UV rays and a wide-brimmed hat can help reduce exposure to irritants.
3. Anti-inflammatory drops: In some cases, anti-inflammatory drops may be prescribed to reduce the inflammation and discomfort associated with pterygium.
4. Surgery: If pterygium causes significant visual disturbance, persistent symptoms or is expanding toward the cornea, surgery may be needed to remove it. Pterygium surgery is performed by an ophthalmologist and is usually an outpatient procedure.